3D Graphy organised a session on 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing for the officers of Cochin Shipyard. The session likely focused on introducing these technologies, discussing their applications in the maritime industry, and exploring how they can benefit shipbuilding and repair processes. This type of session would typically cover topics such as rapid prototyping, customized parts manufacturing, and the potential for reducing costs and improving efficiency in shipyard operations.
The session was initiated by Mr. George John Kochukaleekal, BE Mech, Chartered Engineer, FIE, FIMarE, FIOV ( Valuation), Certified Lloyd Quality Assurance Auditor for Quality, Safety, Environment, Certified Member Institute Arbitration and Mediation of India. Licensed Marine Chief Engineer from Ministry of Marine Department Singapore.
Presently he is the Business Associate, Engineering & Marine, 3D GRAPHY LLP promoting the prospects of 3D Printing & 3D Visualisation for Training, Research and Business with the interest of setting up 3D GRAPHY HUB’s in various organisations and centre’s in India both Engineering and Medical. Since 3D technology is not confined to only one specialisation or sector the scope is immense and it is 3D Graphy’s clear intent to propagate 3D technology across industries. As the credit line of 3D Graphy say’s it all – ” Democratising 3D technology to benefit all”
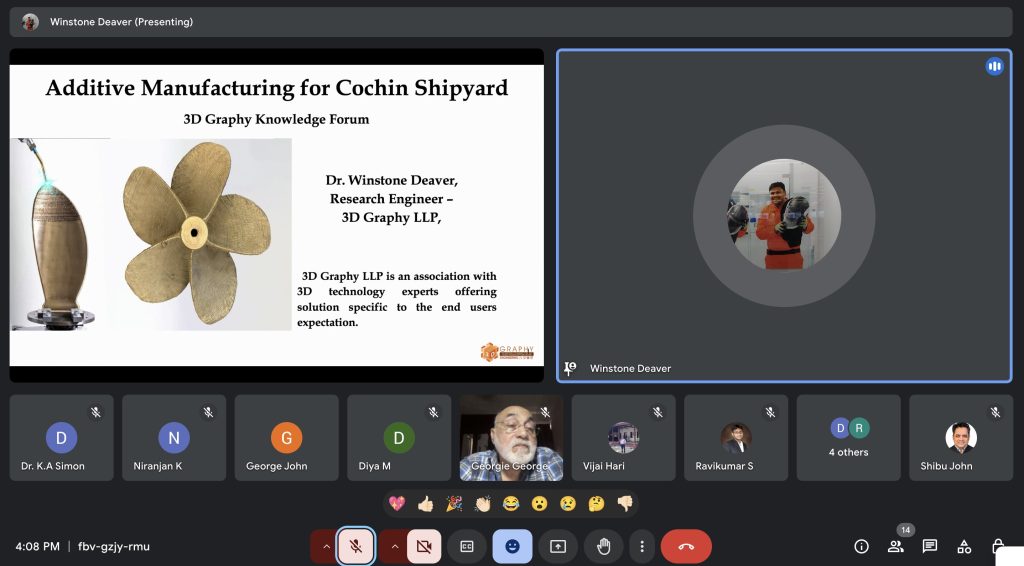
Other team members from 3D Graphy who joined the meeting included Dr. Shibu John, CEO & Founder, 3D GRAPHY LLP, Founder & Secretary, 3DPERA, Organising Committee Member – 3D GEM 2024, Cmde. Niranjan Khardenavis, ( Retd.) Ex- CTO, Indian Navy, Associate Director, Defence & Marine, 3D GRAPHY LLP, Dr. Winstone Deaver, PhD Additive Manufacturing, Research Engineer, 3D GRAPHY LLP, Ms. Tejal Modi, Head PR & Communications, 3D GRAPHY LLP, Editor, 3D Graphy News.
Members from Cochin Shipyard and other dignitaries who joined included Dr. K L Simon, Ex Chief Marine Engineer, Ex Principal Surveyor DG Shipping Mumbai, Ex- Chairman Lakshadweep Shipping, Ex-Director/ Eurotech Marine College, Cochin University Science and Technology Marine Engineering college. Presently Chairperson of Maritime University Cochin.
3D printing technologies offer several benefits and advantages for shipbuilding and boat making, making them increasingly valuable in the maritime industry. Here’s how they can be useful:
1. Rapid Prototyping
- Benefit: Allows shipbuilders to create scale models of ships and boat components quickly.
- Advantage: Enables faster design iterations, leading to more efficient design processes and reduced time to market.
2. Customization and Complex Geometries
- Benefit: 3D printing allows for the creation of complex, customized components that would be difficult or impossible to manufacture using traditional methods.
- Advantage: Facilitates the production of unique parts tailored to specific vessels, improving performance and reducing material waste.
3. Reduced Material Waste
- Benefit: Additive manufacturing (AM) adds material layer by layer, using only what is necessary.
- Advantage: Minimizes waste compared to traditional subtractive manufacturing methods, leading to cost savings and a more sustainable production process.
4. On-Demand Production
- Benefit: Components can be printed as needed, reducing the need for large inventories of spare parts.
- Advantage: Leads to lower storage costs and faster response times for repairs and maintenance.
5. Lightweight Structures
- Benefit: 3D printing allows for the creation of lightweight, yet strong, components.
- Advantage: Contributes to the overall weight reduction of the vessel, which can improve fuel efficiency and reduce operational costs.
6. Enhanced Design Flexibility
- Benefit: Complex designs that would be challenging to achieve with traditional methods can be easily realized with 3D printing.
- Advantage: Enables innovative designs that can improve the hydrodynamics, strength, and functionality of ships and boats.
7. Cost-Efficient Prototyping and Tooling
- Benefit: 3D printing can be used to create molds, jigs, and fixtures needed for the production of ship components.
- Advantage: Reduces the costs and lead times associated with traditional tooling, making the production process more flexible and cost-effective.
8. Integration of New Materials
- Benefit: Advanced 3D printing technologies can work with a wide range of materials, including metals, composites, and polymers.
- Advantage: Allows shipbuilders to experiment with new materials that offer better performance, corrosion resistance, or other desirable properties.
9. Simplified Supply Chains
- Benefit: The ability to print parts on-site reduces the reliance on complex supply chains.
- Advantage: Decreases lead times and the risk of supply chain disruptions, which is particularly beneficial in remote or maritime environments.
10. Improved Maintenance and Repairs
- Benefit: 3D printing can be used to produce replacement parts on demand, even in remote locations.
- Advantage: Shortens repair times and extends the operational life of vessels by making it easier to replace worn or damaged parts.
Overall Impact on Shipbuilding and Boat Making
3D printing and additive manufacturing offer a transformative potential in shipbuilding by enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and enabling the creation of more innovative and sustainable vessels. As these technologies continue to evolve, their adoption in the maritime industry is expected to grow, further driving improvements in design, production, and maintenance processes.



In additive manufacturing (AM), a variety of materials are used depending on the specific requirements of the application. Here’s a look at some of the materials like cupronickel and phosphor bronze, along with others that are commonly used in AM, particularly in industries like shipbuilding, aerospace, and automotive:
1. Cupronickel (Copper-Nickel Alloys)
- Composition: Typically contains 70-90% copper and 10-30% nickel, with small amounts of other elements such as iron and manganese.
- Uses in AM: Cupronickel is used in 3D printing for marine applications due to its excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in seawater environments. It’s ideal for parts like propellers, piping, and heat exchangers.
- Advantages:
- Corrosion Resistance: High resistance to corrosion in seawater, making it perfect for marine applications.
- Thermal Conductivity: Good thermal conductivity, beneficial for heat exchangers and other thermal applications.
- Biofouling Resistance: Reduces the adherence of marine organisms, which is critical in ship components exposed to seawater.
2. Phosphor Bronze
- Composition: An alloy of copper with 0.5-11% tin and 0.01-0.35% phosphorus.
- Uses in AM: Phosphor bronze is often used in 3D printing for creating components that require high wear resistance, such as bushings, bearings, and springs.
- Advantages:
- Wear Resistance: Excellent wear resistance, making it suitable for moving parts.
- Fatigue Resistance: High fatigue resistance, beneficial for components subjected to repetitive stresses.
- Corrosion Resistance: Good resistance to corrosion, particularly in environments with saltwater or chemicals.
3. Stainless Steel
- Composition: An iron-based alloy typically containing 10.5-30% chromium, along with other elements like nickel and molybdenum.
- Uses in AM: Widely used in a range of applications from aerospace to medical devices due to its strength and corrosion resistance.
- Advantages:
- High Strength: Provides durability and resistance to deformation.
- Corrosion Resistance: Excellent corrosion resistance, especially in harsh environments.
- Versatility: Can be used in various industries, including marine, automotive, and medical.
4. Aluminum Alloys
- Composition: Typically composed of aluminum with additions of elements like silicon, magnesium, and copper.
- Uses in AM: Popular in aerospace, automotive, and lightweight structural components due to their low density and high strength-to-weight ratio.
- Advantages:
- Lightweight: Reduces overall weight, improving fuel efficiency in aerospace and automotive applications.
- Good Mechanical Properties: High strength-to-weight ratio and good machinability.
- Corrosion Resistance: Naturally forms a protective oxide layer, enhancing its corrosion resistance.


